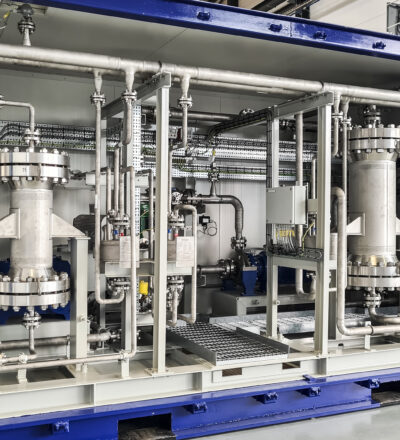
The large-scale production of hydrogen from renewable power sources is key to reducing CO2 emissions related to industrial activity, where hydrogen is a sustainable industry feedstock as well as a renewable energy carrier. When producing such green hydrogen using large-scale electrolysers, fluctuations in the availability of wind and solar power must be taken into account.
In short:
- Researching and modelling the impact of variable operation on large-scale test electrolyser performance for green hydrogen.
- Optimal control strategies will be developed with the goal to improve operational efficiency.
Large scale production of Green Hydrogen
Current available electrolyzer technology, however, benefits from a continuous, well controlled operation within relatively narrow process windows regarding temperature, pressure and flow. At optimally efficient operation conditions, these windows are often close to threshold values regarding materials degradation or safety.
Even though advances in materials and system construction will make future electrolysers more resilient and widen the operating envelope, future systems will still have a trade-off between wear and efficiency. It is therefore crucial to optimize the dynamic and flexible operation of electrolysers to ensure their reliable and efficient operation. In this project, dynamic behaviour and control optimization of dynamic parameters will be studied, modelled and tested to create a more efficient overall system that mitigates fluctuating demand and supply.
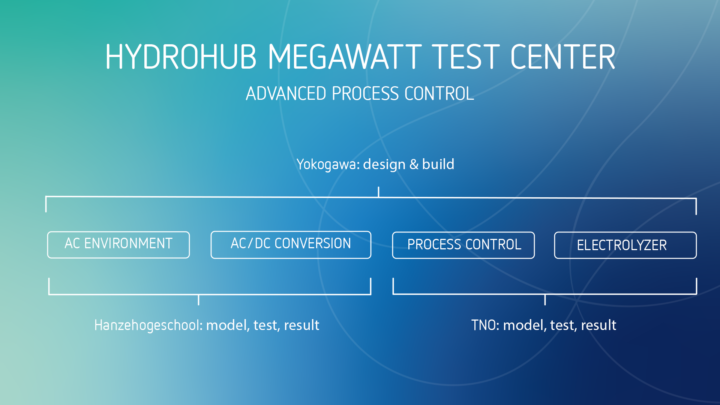
Advanced Process Control
The employment of Advanced Process Control can lead to the improvement of process efficiency by optimizing multiple parameters simultaneously, based on real-time evaluation of process dynamics, interaction, and buffering and release of mass and energy in reactions. This has been successfully implemented in other industries, but for electrolysers producing green hydrogen it is a totally new way of process control. It is expected that it can result in 2 to 3% operational efficiency gain.
The main objective of this project is to develop and implement a multi-variable, model based Advanced Process Control concept for electrolyser systems that will optimize production while staying within material and safety thresholds. The PEM unit at the MegaWatt Test Center will be used to test implementation and validate results. Hanze University of Applied Sciences will be responsible to support the field measurements, the hardware and model development. TNO will develop the advanced control model in an interactive process with project partners.
Hydrohub MegaWatt Test Center
The Advanced Process Control project is a dedicated addition to the Hydrohub MegaWatt Test Center project and will be executed in parallel and without effecting the time frame of the current HydroHub MegaWatt Test Centre projects. Located at the Zernike campus of Hanze University of Applied Sciences in Groningen, the MegaWatt Test Center focuses on the operation and performance of small industrial PEM and Alkaline units of 250 kW each and offers an open-innovation ecosystem supporting further advanced technology development for electrolysis.
With participation of Shell, Nobian, Yara, Gasunie, Frames, Groningen Seaports, TNO, Hanze University of Applied Sciences, University of Groningen and Yokogawa, it forms part of ISPT’s Hydrohub Innovation Program aimed at developing large-scale, electrolysis-based production of sustainable and low-cost hydrogen, as a driver for circular industrial chains.
Interesting reads on Hydrogen
- Launch of the Green Ammonia Innovation Platform
- How to meet the Green Hydrogen demand of the future?
- 10 years of hydrogen: 3 highlights that involved ISPT
Our join our Hydrogen LinkedIn-community.
You might also be interested in
Acknowledgement & partners
This project is co-funded by TKI-E&I with the supplementary grant 'TKI- Toeslag' for Topconsortia for Knowledge and Innovation (TKI’s) of the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Policy.













