Farming and food production globally contribute significantly to human-caused greenhouse gas emissions, alongside fossil fuels and major deforestation. A transformation of food, land use, and water systems is needed to drastically reduce climate impact, restore nature and biodiversity and improve the living standards of 600 million farming families worldwide. This will enhance climate resilience and ultimately secure global food production for the future. This is called the agrifood transition.
Well-functioning food and agriculture systems are crucial for the food security, health, and livelihoods of the global population, which is currently 8 billion and expected to reach 9 or even 10 billion by 2050. These systems are severely impacted by climate change (think of soil erosion, desertification, extreme weather, etc.).
Farming and the processing of food are responsible for around 30% of global human-made emissions, which could increase as food demand grows with the population. Farmland is expected to expand by about 10% by 2030, putting further pressure on ecosystems and potentially increasing deforestation.
First step: regenerative agriculture
What is needed, first and foremost, is a transition to regenerative and circular food and agriculture systems. Regenerative agriculture is a collective term for farming practices that not only minimize the negative effects of conventional agricultural practices but also aim to positively contribute to nature, the environment, climate, food security, and the social and economic conditions of farmers and agricultural communities.
The starting point of regenerative agriculture is to work on healthy, vital soil, thereby creating a sustainable and resilient ecosystem where all soil functions are optimized: primary production, carbon regulation, water management, nutrient cycles, and biodiversity. Importantly, such a system must provide sufficiently for farmers without depleting scarce natural resources.
Second step: protein transition 60%-40%
Secondly a shift in protein consumption is necessary, due to climate concerns, increasing scarcity of natural resources (like land and water) and an increase in population. Within Fascinating we aim at high quality and nutritional food, which means that consumers should find a balance between proteins from plant sources (like legumes and grains) and animal sources (meat, fish, dairy and eggs).
Even though animal protein is part of a healthy diet, the long term goal according to Dutch Grondstoffenakkoord (2018) is reversing the ratio in animal/plant protein consumption from 60/40 to 40/60. In this way, we can feed the growing population with healthy food and maintain a healthy planet.
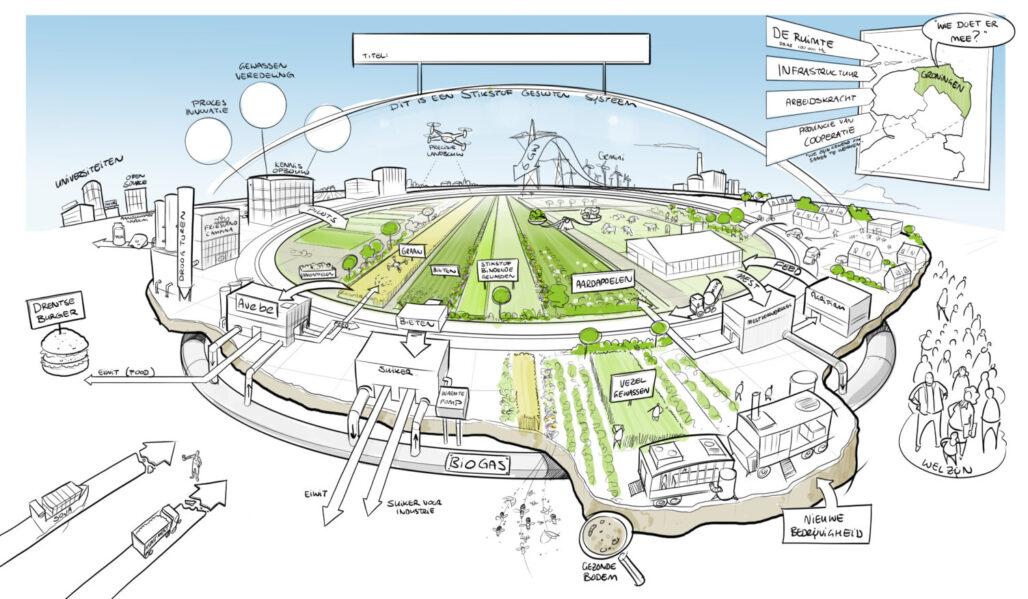
Fascinating Groningen Program
The Institute for Sustainable Process Technology (ISPT) collaborates with farmers, processing companies, SMEs, academic institutions, and other partners through the ‘Fascinating’ program to develop a regenerative and circular agriculture system. Focused on high-quality protein crops, such as field beans, these initiatives aim to contribute to the protein transition and improve the quality of meat, dairy, fish, and egg substitutes. Groningen is chosen for its unique combination of a strong agricultural sector, large-scale industrial infrastructure for processing food crops and biomass, sustainable energy availability, a developed chemical sector, and leading academic institutions.
The Fascinating program, which stands for ‘Food Agro Sustainable Circular Nature Technology in Groningen’, aims to create a regenerative and circular agriculture system with 5 subgoals, addressing the challenges for the next 25 years.:
- High-quality nutritional products
- Sustainability and nature inclusion
- Circularity/closed-loop agriculture
- Soil health
- A sustainable income model for farmers and agri-food businesses in Northern Netherlands
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
In September 2023, ISPT received the SDG Predicate in recognition of its contribution to the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through the Fascinating program, described as a unique initiative driving food and agriculture transition in Groningen and making a significant difference in sustainability dimensions.
The jury praised Fascinating not just for its focus on sustainable agriculture but also for achieving concrete results and raising awareness about healthy and sustainably cultivated crops, significantly influencing farming practices.
Our role in the agrifood transition
Together with our stakeholders, the Institute for Sustainable Process Technology (ISPT) is involved in establishing the infrastructure that is needed for the agrifood transition.
ISPT, serving as a platform and network organization, prioritizes key principles, including independence, interdisciplinary collaboration, expertise, and the nurturing of mutual trust. These principles are indispensable for ISPT to collaborate effectively with innovation partners, achieve its intended outcomes, and have a significant impact in the realm of the energy transition, as well as the vital transitions in materials and sustainable agriculture.
We feel at home in complex projects involving multiple actors and stakeholders. Within our network and programs we work on new, feasible and innovative solutions that will lead to full circularity by 2050. We are the director of the new economy.



