As the global population continues to grow, the imperative to feed the world while respecting the limits of the ecosystem becomes increasingly urgent. This necessitates a fundamental redesign of our food industry, focusing on sustainable practices that maximize nutritional value and minimize waste. A huge task that no sole company can easily undertake on its own. That is why the Institute for Sustainable Process Technology (ISPT) unites parties from both the food industry and beyond to tackle this task together.
Recognising the magnitude of this task, the Institute for Sustainable Process Technology (ISPT) has convened stakeholders from the food industry, universities, government and other sectors to collectively confront these challenges. By fostering collaboration and innovation, ISPT aims to develop solutions that ensure the long-term viability of food production within the boundaries of the ecosystem.
In a time when the agricultural and food production sector is responsible for approximately 30% of global greenhouse gas emissions, we are in need of refreshing perspectives on sustainability.
Peter de Jong – Expert on Food and Agriculture, Fascinating
Dutch food industries
Despite our small size, the Netherlands is a significant force in the realm of food production. Renowned as a global powerhouse in agrifood and agtech innovation, the country boasts impressive achievements:
- Ranking 2nd in worldwide agrifood exports, thanks to cutting-edge farming techniques and innovative food technologies.
- Hosting the production and research facilities of the top 10 agrifood corporations globally.
- Leading the world in agrifood research and development investment.
- Home to Wageningen University and Research, acclaimed as the premier institution in agrifood studies globally.
- Aiming to spearhead global circular agriculture initiatives by 2030.
- Backed by governmental support for research and development in alternative protein sources.
The need for sustainability in our current food system
The achievements of Dutch agricultural are notable. Boasting an impressive annual output of €65 billion in agricultural produce, this sector comprises a formidable 17.5% of the nation’s total exports. Moreover, the agricultural and horticultural sectors collectively contribute a formidable 10% to the Dutch economy, employing a substantial portion of its workforce.
However, the production of food comes with its toll: Farmers use energy, water and other resources to produce food. Food production also generates waste and contributes to national emissions. According to RVO, more than half of the emissions in the agricultural sector originate from livestock farming. This is mainly due to methane. Additionally, almost a quarter of the emissions come from crop cultivation, primarily from nitrous oxide, which arises in the soils of fields and grasslands due to nitrogen fertilization. Finally, just over a quarter comes from greenhouse horticulture, due to natural gas consumption for heating greenhouses and generating electricity.
At the climate conference in Paris (2015), agreements were made to limit global warming by reducing the emission of greenhouse gases. A decrease in emissions from agriculture is crucial within this framework. Empowering this endeavor rests not only on the shoulders of farmers but also on the proactive engagement of companies and (local) Government.
Source: Rijksoverheid, RVO
Our vision: Agrifood transition
A transformation of food, land use, and water systems is needed to drastically reduce climate impact, restore nature and biodiversity and improve the living standards of 600 million farming families worldwide.
One important step is the transition to regenerative agriculture, which enhances ecosystems while supporting farmers. By prioritizing healthy soil, regenerative practices optimize primary production, carbon regulation, water management, nutrient cycles, and biodiversity. This ensures sustainability without depleting natural resources.
A second crucial step is the protein transition, shifting from animal-based to plant-based protein sources. Currently at 60% animal protein to 40% plant-based, the aim is to reverse this to 60% plant-based and 40% animal protein, known as the protein transition.
This combined is what we call the agrifood transition: Together with our stakeholders, the Institute for Sustainable Process Technology (ISPT) is involved in establishing the infrastructure that is needed for the agrifood transition. Together with our partners we are working on growing crops on healthy soil that are high in proteins and can therefore be part of a healthier diet. As a result, less animal-based products need to be consumed in order to get the right amount of nutrients.
The food industry applies process technology to meet the nutritional needs of the growing world population. But with food processing come sustainability issues, in particular in energy and water use.
So the the food industry will play a crucial role in establishing a sustainable society by 2030:
- How can we reduce our energy use in the production process?
- How can we adjust packaging?
- How can we close the nutrient cycle?
- Do we use fossil or renewable energy?
- Can we improve the design of the dryer?
- Can we use a different drying processes, like extracting water with a high capacity membrane system?
- What about sustainability at the farm, like carbon footprint reduction, biodiversity, and landscape and nature preservation?
How do we reach our 2050 goals: A roadmap
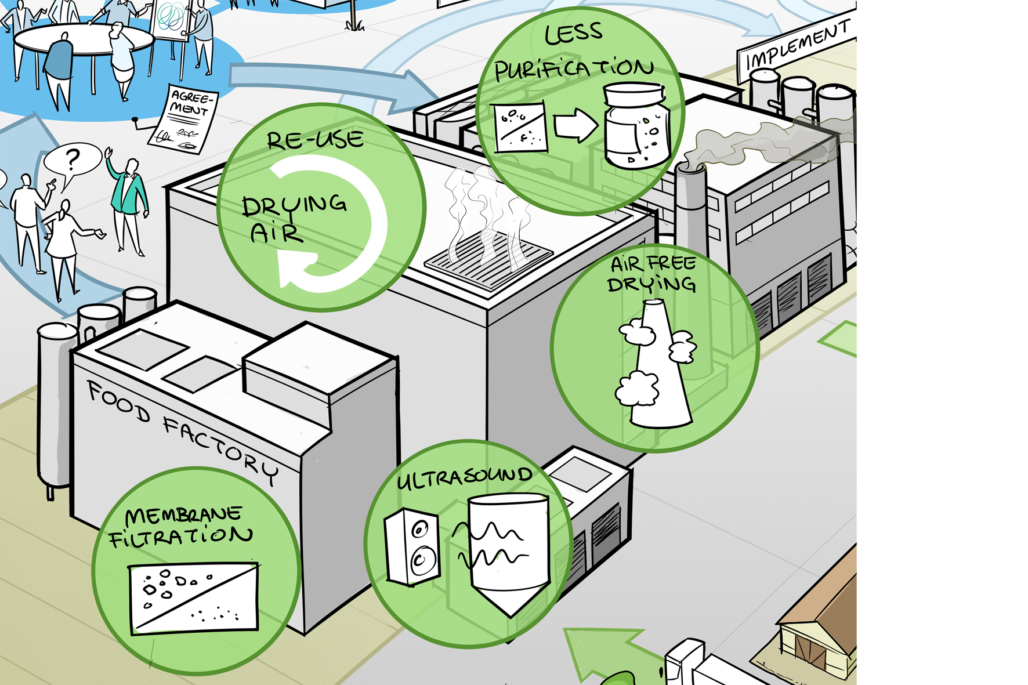
The innovations we need to reach our goals, include technological advancements such as:
- air-free drying without CO2 emissions;
- re-use of drying air;
- optimization of membrane filtration;
- utilization of emerging technologies such as ultrasound in dewatering; and reduced purification.
- Integral to our vision are the implementation of advanced self-learning digital technologies in process control systems and the electrification of processes. These innovations are among the key drivers for achieving sustainable food processing in the future. Other fundamental aspects are improving energy efficiency, minimizing waste streams, and optimizing raw materials.
We designed this roadmap in cooperation with technical universities, NIZO Food Processing, Wageningen University, WFBR, food technology providers, innovative SMEs, and other experts.
What do we want to achieve?
By 2050, the food industry aims to achieve an 80% reduction in energy consumption and CO2 emissions. Full utilization (100%) of raw materials and crops, and the production of high-quality goods. All while ensuring consumer satisfaction and health. Achieving these goals requires innovation. To maintain this leadership position, we must remain focused on the path to our 2050 goal.

How do we reach our 2050 goals?
Integral to our vision are the implementation of advanced self-learning digital technologies in process control systems and the electrification of processes. These innovations are among the key drivers for achieving sustainable food processing in the future. Other fundamental aspects are improving energy efficiency, minimizing waste streams, and optimizing raw materials.
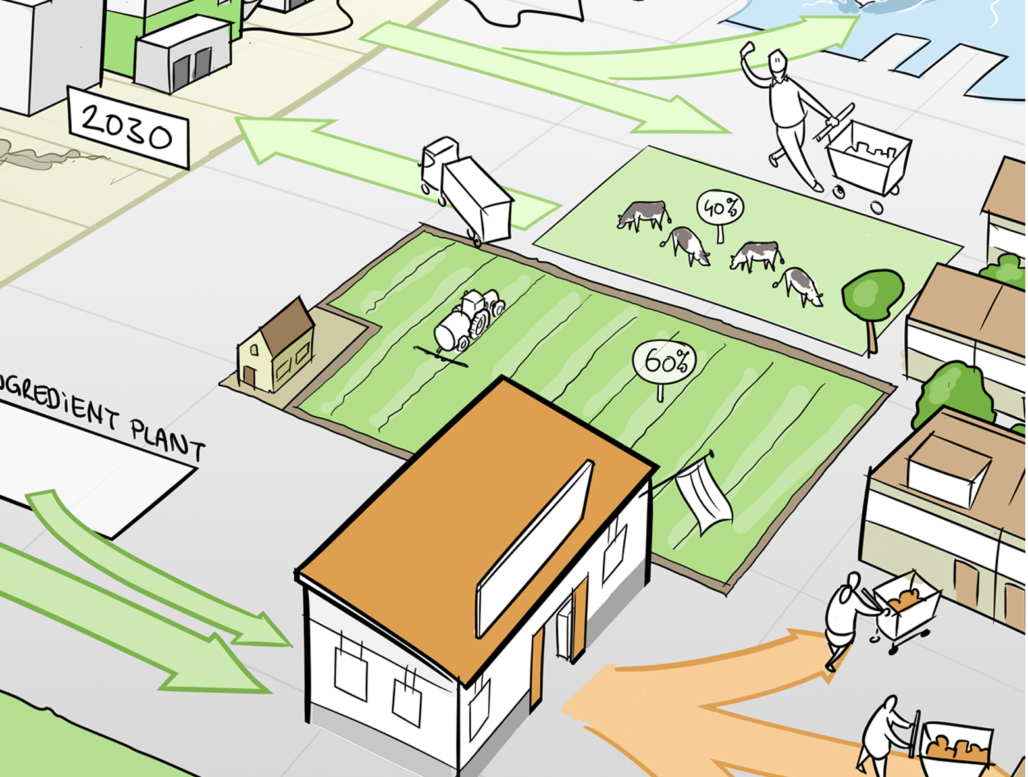
From 40% plantbased to 60%
The agri-food transition requires a shift from 60% bovine proteins to 40% and from 40% plant proteins to 60%. Reducing pasture production and expanding the cultivation of plant proteins in rotating crops are necessary steps to decrease greenhouse gas emissions and enhance biodiversity.
Our programs
Fascinating: the agricultural sector of the future
Based in Groningen, ISPT is involved in the Fascinating project together with the three agricultural cooperatives (Agrifirm, Avebe andCosun, ), LTO Noord, Rabobank, Invest-NL, several different knowledge institutes, the Province of Groningen and more than 80 farmers. Together, they are working on our future agricultural system: a circular system that balances sustainability, nature, healthy food, and economic impact. This features a closed nitrogen cycle and no CO2 emissions. Fascinating is an open test and innovation program that connects farmers, companies, knowledge institutions, and the community.
Drying and dewatering: improving energy consumption in the food transition
Drying and dewatering is the most energy intensive process in the food industry, improving these technologies will have an enormous effect on sustainability. Our vision is a future where process technologies are the driving force behind a sustainable food transition, with a particular emphasis on minimizing energy consumption.
We strive for the development and implementation of advanced technologies that not only increase the efficiency of food production but also maximize the use of renewable energy sources. Through this focus, we aim to play a leading role in shaping a food system that is not only resilient and ecologically responsible but also energy-efficient, thereby ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.
Drying and dewatering is the most energy intensive process in the food industry, improving these technologies will have an enormous effect on sustainability
Peter de Jong – expert on food and agriculture
Mild Fractionation for Food: closing the nutrient cycle
Where in the Drying & Dewatering program the focus is on energy reduction, in the program Mild Fractionation for Food we work on closing the nutrient cycle. Fractionation refers to the extraction of valuable components like proteins and other fractions from residual flows, beet leaf and grain waste for instance. Mild refers to the way it is processed.
It is our mission to explore new concepts and technologies for the extraction of complex molecules and proteins from various process flows, and help companies in the food industry to achieve their sustainability and business goal.
Heat: state of the art heat integration technologies
Numerous companies in the agro-food, horticultural, and food sectors primarily use energy for heat generation. To aid these industries, alongside the paper and chemical sectors, in meeting the CO2 reduction targets for 2030 and 2050, the Institute for Sustainable Process Technology has spearheaded the establishment of a national cross-sectoral Heat Integration Platform.
Participation in the platform provides all of these industries with a knowledge base to identify relevant heat integration developments for their operations. This aids in preparing company-specific CO2 plans, deciding on participation in joint R&D programs, and evaluating technological investments.
Climate agreement
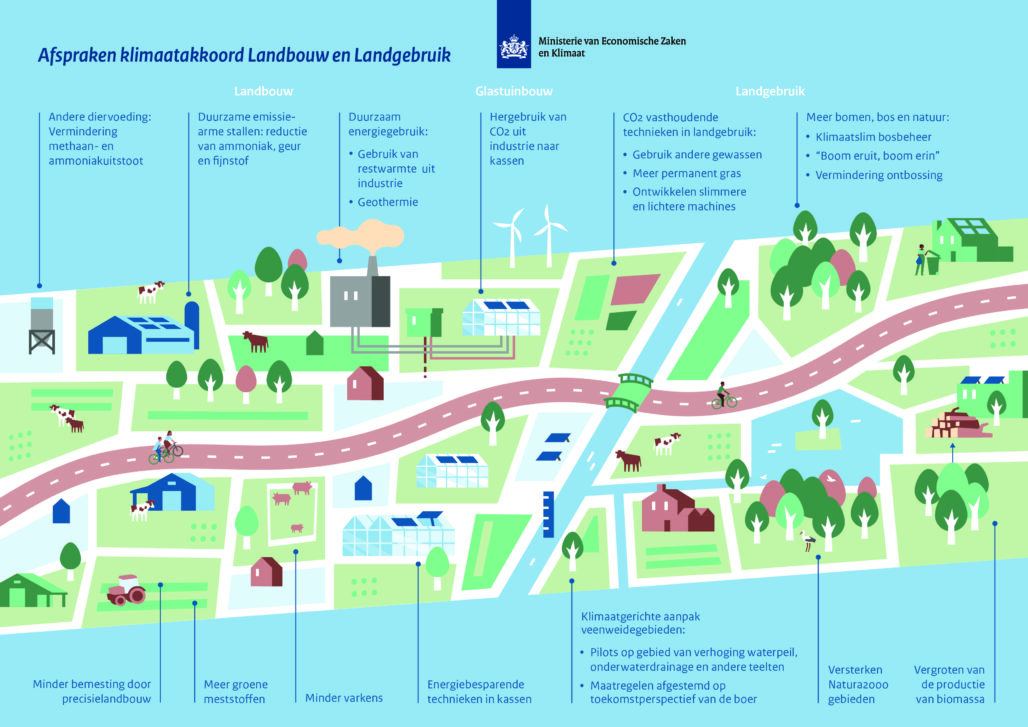
According to the Climate Agreement, agriculture and land use must be climate-neutral by 2050. This is a complex challenge, as some greenhouse gas emissions are unavoidable: cows produce methane, and nitrous oxide is released from synthetic fertilizers, both of which are greenhouse gases. On the other hand, the sector also sequesters CO2 in trees, soil, and grass, contributing to the reduction targets. The agricultural sector plays a significant role in achieving climate goals. The Climate Agreement states: Innovative chains and companies are needed to realize this vision and ambition for 2050, as well as to achieve the interim targets for 2030. Parties in the Climate Agreement are therefore focusing on innovations for:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the production of food and non-food by 2050;
- Promoting (regional) land-based practices while closing nutrient cycles;
- Achieving net production of renewable energy from the agriculture, horticulture, and forestry sectors;
- Structuring the Dutch land and water surfaces for CO2 sequestration and use;
- Halving the climate impact of purchasing choices by Dutch consumers by 2050.
Source: Klimaatakkoord
The future of agriculture
The focus of our agricultural sector has long been on scale and efficiency. However, this often came at the expense of nature and soil quality. The focus for the future must shift to the added value of the products we create in terms of nutritional and economic value, within a completely circular system with minimal footprint. A system that generates less nitrogen and CO2 emissions. The agriculture of the future rests on four pillars:
- Healthy and balanced nutrition: We are making the shift from quantity to quality. How can we translate a healthy diet into our agricultural system? What does the consumer want?
- Sustainable production of nutritional crops: We express quality in terms of nutritional and economic value. How can we balance food production with nature, without CO2 or nitrogen emissions, and with enhanced biodiversity?
- Energy-efficient and sustainable processing: Current processing methods result in significant nutrient loss and high energy consumption. By making existing technologies more energy-efficient and developing new technologies, we can utilize all nutrients in an energy-efficient manner.
- Non-food use of residual streams: After processing agricultural products, a substantial residual stream remains that cannot be used for human or animal consumption, such as cellulose, soil, and manure. We use these residual streams circularly as raw materials for the chemical industry or as an energy source.
Dutch Climate Agreement Roadmap
Interesting podcasts and reads
- Podcast: NIZO Talks Food and Health
- Podcast (in Dutch): Toekomst van Ons Eten
- Podcast: Investing in Regenerative Agriculture and Food
- National Geographic: This Tiny Country Feeds the World



