The industry in the Netherlands accounts for approximately 45% of total energy use. The electrification of industrial processes can make a substantial contribution to reducing our national CO2-emissions, thereby aligning with the energy transition objectives for 2030: a 40-50% reduction in CO2 emissions compared to 1990 levels. At the moment, the Dutch industry has already achieved successful electrification through the implementation of electric drives and monitoring equipment.
At ISPT, the focus lies on the next wave of electrification that focuses on shaping more sustainable production methods and heating processes. Known as Industrial Electrification or Power-2-X, this paradigm shift involves replacing fossil fuel-driven processes with those powered by clean electricity or other green molecules.
What is Industrial Electrification?
Electrification of industrial processes refers to the systematic transition from conventional fossil fuel-based energy sources (such as oil, gas, and coal) to the utilization of electricity or green energy sources (such as renewable electricity, green molecules or hydrogen) to power various stages of manufacturing, production, heating and other industrial operations. This transformation encompasses the conversion of existing processes, machinery, plants and equipment to run on electricity, as well as the implementation of new, innovative electrified technologies, with the overarching goal of achieving increased energy efficiency, reduced carbon emissions, and a more sustainable industrial landscape.
The use of sustainable electricity can significantly lower the CO2-footprint of the Dutch process industry. And since this industry accounts for over one-third of total energy use in the Netherlands, this will also make a substantial contribution to reducing the national CO2-emissions. However, shifting towards renewable electricity sourced from solar and wind requires significant restructuring of energy-intensive processes. This transition poses major challenges to the energy supply chain. Society must ensure that the future energy system is robust and capable of supporting all stakeholders, including industry, transportation/mobility, and the built environment.
Dutch industry has traditionally run on a combination of natural gas and large quantities of residual gases. We need to restructure our energy-intensive processes and use more renewable electricity from solar and wind. This is a major challenge to the energy supply chain. The future energy system needs to be robust and support all stakeholders: industry, transportation/mobility, and the built environment.
We need electrification to achieve Dutch climate goals
Our vision
In today’s modern society, the process industry drives the production of essential goods. Yet, this progress is coupled with a substantial energy consumption and the resulting CO2 emissions. Electrifying the process industry emerges as a pivotal transition pathway towards fostering a sustainable energy landscape, under the assumption of future availability of entirely sustainable or CO2-neutral electricity. Maximizing the potential of this transition demands bold system and process innovations.
In order to achieve industrial electrification the entire value chain works together. Collaboration is the keyword.
This is where ISPT can play a major role: we feel at home in complex projects involving multiple actors and stakeholders. Within our network and programs we work on new, feasible and innovative solutions that will lead to full circularity by 2050. We are the director of the new economy.
The challenge lies in acceleration
Electrification technologies are readily available. However, the challenge lies in acceleration. For an electrified industry, we need sustainable sources as alternatives to fossil fuels. This can for example be sourced from offshore wind energy. Wind farms generate a substantial amount of power, and the industrial sector transitioning to sustainability requires significant electricity. A seamless deployment of wind farms is not guaranteed. The electricity price determines the viability of projects. For industry, electrification is a serious option, provided it is more cost-effective than other solutions. However, while a high electricity price benefits the business case for wind energy, it is not attractive for electrification. This creates a split incentive. Thus, a situation can arise where collaborating parties within a chain end up waiting for each other.
It is also important to increase the demand for sustainable electricity, to ensure that investing in sustainable generation remains attractive. Industrial electrification is crucial in this regard; industry often continues to rely on fossil fuels such as natural gas. Electrification in industry can lead to a short-term reduction of 9 to 20 million tons of CO2 emissions. At the same time, industry will electrify only if there is sufficient sustainable electricity available. Government intervention is necessary to shape policies in this area.
Integrated approach
At the ISPT we contribute to the energy transition from the perspective of the process industry. We are convinced that to reach the 2050 targets of up to 95% emission reduction, it is imperative to completely re-imagine and re-invent production chains, tuned to the transitions in the energy system. This is what we call system integration.
This entails identifying and developing the key enabling technologies for carbon-neutral industries, establishing their potential relevance and understanding how they can be implemented in an industrial environment. It also requires an analysis of the context governing this implementation:
- The context of the current industrial environment;
- The context of the future energy system;
- and the context of the envisioned energy-industry value chain.
All this will lay the foundation for technology development towards actual demonstration at industrially relevant scales. A striking example of the latter is in the field of hydrogen, where we operate the Hydrohub Innovation to achieve affordable large-scale water electrolysis in an industrial setting.
Supply and demand, the new mix of energy carriers: everything is interrelated
Andreas Ten Cate, in his article Embrace the complexity of the energy transition
Governmental support: Rijksoverheid and electrification roadmap for industry
A goal of Rijksoverheid is to enhance sustainability and reduce CO2 emissions in the industrial sector. One strategy to achieve this is through the electrification of industry. In 2022, Rijksoverheid published the Electrification Roadmap, a carefully developed and detailed plan outlining the most promising pathways to reach sustainability targets by 2030 and 2050.
To keep the 2030 goals within reach, accelerating electrification in the industry is a top priority
– Cora van Nieuwenhuizen, Chairman of Energie-Nederland
Collaboration is the keyword for electrification in the Dutch process industry
In order to achieve industrial electrification the entire value chain works together. Collaboration is the keyword.
This is where ISPT can play a major role: we feel at home in complex projects involving multiple actors and stakeholders. Within our network and programs we work on new, feasible and innovative solutions that will lead to full circularity by 2050. We are the director of the new economy.
ISPT takes a leading role in developing the technologies for the envisioned energy-industry value chain:
Sustainable hydrogen
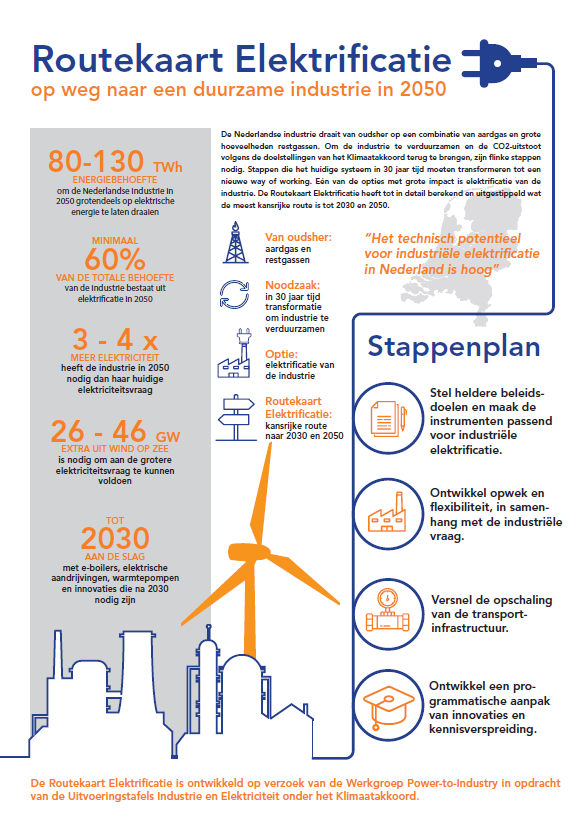
To drastically reduce the amount of CO2 emissions in the Netherlands through electrification, we will need an additional capacity of 130 TWh by 2050. This is on top of the existing electricity demand from industry and the growing demand from other sectors such as data centers.
ISPT takes a leading role in developing the technology for our future energy system. For example by designing an advanced green hydrogen plant at gigawatt scale. This design is part of ISPT’s Hydrohub Innovation Program and will be the foundation for the hydrogen economy of the future.
Drying and Dewatering
When it comes to reducing energy use and CO2 emissions of industry, innovations in drying and dewatering play a key role. Drying and dewatering are important processing steps in industry. All kinds of products require drying, varying from vegetables and dairy products to paper and sewage.
However, drying is an energy-intensive technology, requiring 80 PJ a year (2013 NEVI). In fact, it is one of the most energy-consuming processes in the process industry, especially in the food and paper industries. When it comes to reducing energy use and CO2 emissions of industry, innovations in drying and dewatering play a key role. ISPT’s Drying & Dewatering maintains a sustainable innovation program where the focus on reducing energy and costs use is strongly linked to the manufacturing of high quality and sustainable products.
Separations for Circularity
The process industry needs to transition to a circular economy, where renewable resources become the norm. This also means that future industrial plants and clusters will need to have minimal discharge and lower carbon and water footprints. Our seperations for circularity program aims to (1) accelerate the collaborative development of radically innovative technologies for the separation and treatment of fluids; (2) ensure continuity of industrial operations in a changing environment; (3) accelerate the realization of a carbon-neutral and circular industry with a reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
The focus of this program is on intensification and electrification of the separation and treatment of liquids and gases, leading to the energy-efficient production and the recovery and reuse of valuable components. This should enable at least a 49% reduction in CO2 emissions along the total production process by 2030 in comparison to 1990 as set forth in the central goal of the Climate Agreement by the Dutch government.
Heat
Heat is the largest energy consumer for a large number of companies in the agro-food, paper, chemical, horticultural and food sectors. Our Heat program aims to accelerate the development and application of sustainable heat and heat-integration technologies that enable the transition to 100% CO2-free industrial heating.
Climate impact of electrification
The climate impact of electrification is profound and holds promise for significant emissions reductions across various sectors. Over the next 30 years, a transformative shift in energy usage within these sectors is conceivable, leading to a substantial decrease in CO2 emissions. A report titled “Sector Coupling in Europe: Powering Decarbonization,” conducted in collaboration with Eaton and Statkraft, explores the potential of electrification while considering ongoing policy developments in countries like the Netherlands, Germany, and the United Kingdom.
It states that electrification offers a pathway to mitigate climate change through both direct and indirect means. Direct changes could involve the widespread adoption of electric vehicles in transportation or the implementation of electric heating systems, such as heat pumps, in buildings and industrial settings. Meanwhile, indirect changes, like the adoption of “green hydrogen” produced through electrolysis using renewable electricity, present opportunities to decarbonize sectors reliant on fossil fuels for heat generation.
This comprehensive approach to electrification underscores its role as a key driver in achieving climate goals and fostering a sustainable future.
Without electrification it will be difficult to achieve the climate goals
Alice Krekt, Deltalinqs in Collaboration as the keyword for electrification in industry
Towards carbon neutrality in industry
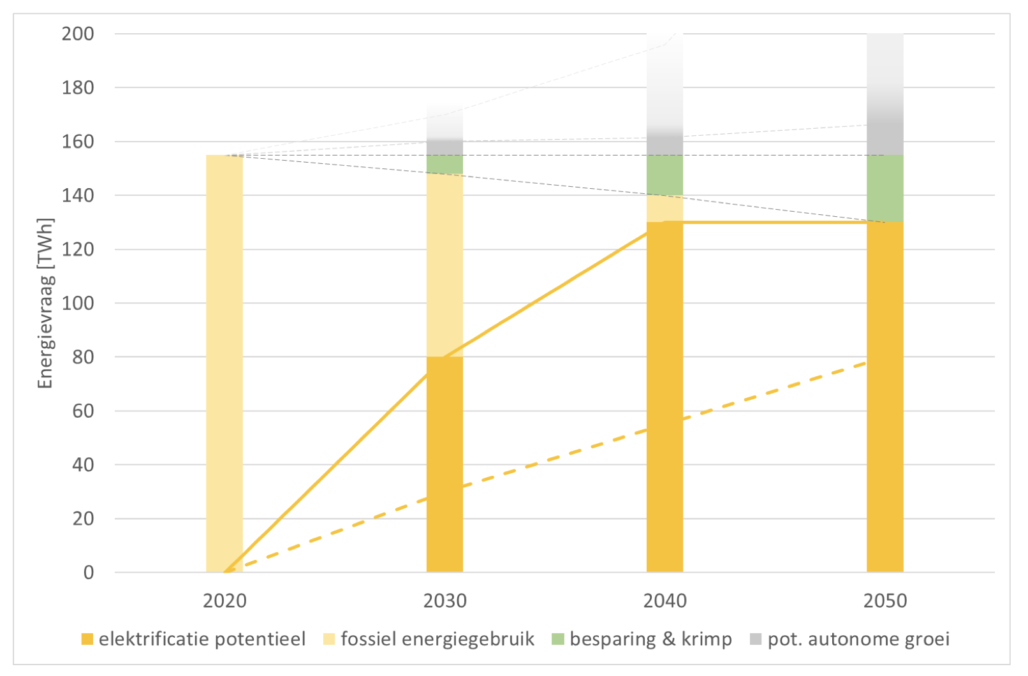
With the aim of becoming climate-neutral by 2050, electrification in the industry will play a crucial role. Statistics of today show that between now and 2030, it should be possible to achieve 30 TWh of electrification, resulting in a reduction of 9 megatons of CO2 emissions. Through the flexible deployment of electric compressors, electric boilers, and heat pumps in combination with gas-fired boilers and CHP (combined heat and power) installations, this could even increase to 80 TWh and achieve an emission reduction of 20 megatons.
After 2030, the technical potential for electrification of large-scale high-temperature processes will increase, with an additional demand for electricity and hydrogen of 40 TWh by 2040, rising to 130 TWh by 2050. Emissions will then decrease to 45 megatons. By that time, it will be technically feasible to electrify processes with high temperatures, including those in the steel industry. Through direct and indirect electrification, the entire industry can operate fully carbon-neutral.
Source: TNO
Industrial electrification in the Netherlands
Large-scale industrial electrification will play a key role in the strategy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the industry. The Netherlands is well positioned for its application. The country boasts a favorable location for both the large-scale production of affordable renewable electricity and hydrogen from North Sea wind, as well as the import and transit of renewable energy carriers via sea routes. Additionally, the Netherlands already possesses a highly developed electricity infrastructure, with a significant amount of cross-border transmission capacity.
Furthermore, the Netherlands serves as the beating heart of the North-West European industrial cluster, with an extensive network for natural gas, energy resources, and industrial gases. In addition to the energy infrastructure, the knowledge infrastructure is also well-suited. The country boasts excellent research and development facilities, including various technical universities, TNO, and the Institute for Sustainable Process Technology (ISPT), which have initiated research programs in the field of industrial electrification.
This presents the Netherlands with a unique opportunity to lead the way, supported by a highly educated workforce, a sophisticated knowledge base, and significant innovation capacity in the energy and industrial sectors. The opportunities for electrification of industrial processes lie in both the direct utilization of electricity and the indirect utilization through conversion to hydrogen. Other emission reduction techniques, such as process efficiency improvements, energy conservation, biomass (green gas), geothermal energy, carbon capture and storage (CCS), and the use of blue hydrogen, will also make significant contributions to reducing CO2 emissions.
Flexibility is key because it can help all stakeholders envisage a single system that is based around green energy and that can operate smoothly, even though it comprises so many elements
Key take away from Grasping the Grid
Source: VNO-NWC
Step-by-step plan for taking advantage of opportunities
Intensive cooperation from all players in the chain will be need in order to take advantage of these opportunities. Government, electricity producers, grid operators, academia, and industry must now start choosing policies and investments that will lead to the rollout of electrification in the near term while preparing the path to 2050. The government has an important role to play here in initiating and coordinating the process, and in creating the right conditions for industrial electrification.
The Roadmap provides a step-by-step plan for industrial electrification:
1. Set clear policy goals, and make instruments appropriate for industrial electrification
Industry should create a minimum of 30 TWh of additional capacity by 2030. Current subsidies (SDE++) should provide greater scope for electrifying industry. In order to achieve the 2030 targets, this push must come within the next two years.
2. Develop generation and flexibility, in keeping with industrial demand
Develop at least an additional 10 GW of offshore wind by 2030. Prepare to create an additional 26 to 46 GW of capacity by 2050. The development of generation and demand will require a national assurance mechanism that will give certainty to both sectors.
3. Accelerate the scale-up of the transport infrastructure
More transmission capacity for electricity and hydrogen infrastructure must be worked on urgently between now and 2030. Decisions on the additional large-scale reinforcement of electricity grids and further strengthening of the national hydrogen infrastructure into a national backbone are needed by 2022. This is why the Roadmap calls for shorter permit processes, and for better and secure data exchange.
4. Develop a programmatic approach to innovations and the dissemination of knowledge
Innovation, scaling up, and reducing risks and costs are key to creating additional capacity on the scale required. This will require a programmatic approach to innovations with a greater commitment to electrification, organizing knowledge exchange between and among companies, and training enough technically qualified people.
How to accelerate: not a time for dithering
It is now up to the government, grid operators, industry, the energy sector, and other stakeholders to put meat on the bone. As the authors of the Roadmap see it, this is no time for dithering. The Roadmap provides the tools needed to get started right away, both to industry and the energy sector, and to government and politicians.
If we want to drastically reduce, through electrification, the amount of CO2 emissions Dutch industry produces, we will need a huge amount of additional generating capacity. That additional amount of electricity that industry will use, both directly and indirectly (via conversion to hydrogen), could reach some 130 TWh by 2050. This is on top of existing electricity demand from industry, demand from new industries, and growing demand from other sectors such as data centers. We are talking about more than the current total electricity consumption in the Netherlands (thus including households, offices, and so on) and 3 to 4 times more than industry’s current electricity demand.
The minimum amount of electricity and green hydrogen that will have to be made available to meet emission-reduction targets, is 80 TWh. This will also require the maximum use of other emissions-reduction options such as energy conservation, green gas, geothermal, and the current CCS cap. The Roadmap concludes that the required 80 TWh for industry is a clear no-regret target, and that it will be very likely still not enough. To meet demand from industry, additional wind turbines will need to be built at sea, generating an additional 26 to 46 GW. In the short term, in the period up to 2030, industry can get started, with hybrid and other e-boilers, electric drives, and heat pumps. Further innovations will be needed after 2030.
What’s next: Embrace complexity
To envision a future powered by a sustainable and efficient energy system, we must confront and unravel the complexities of our current situation, much like addressing a Gordian knot. This challenge, seemingly insurmountable within traditional paradigms, demands innovative thinking and decisive action. How can we ensure we make the right choices? What are the steps we need to take? And how can we confidently navigate towards a future where our energy system is resilient and sustainable?
During our themed session, “How to Unravel the Gordian Knot of the Transition(s),” we delved into these pressing questions. The consensus was clear, according to Andreas Ten Cate: “to progress, we must establish a shared vision of our destination. Leadership is crucial in framing the fundamental questions that guide our journey. Through thoughtful exploration of these questions, we can design effective solutions.”
Transition models are pivotal in this process. They elucidate the intricate connections within the energy system and provide clarity on the consequences of various scenarios. These models are not just analytical tools; they are essential guides that help us make informed choices, ensuring that each step we take moves us closer to untangling the knot and achieving our collective energy goals.
In conclusion, embracing a forward-thinking and collaborative approach, supported by robust transition models, is key to transforming our energy landscape. Together, we can navigate this complex journey, making strategic decisions that lead to a sustainable and electrified future.




