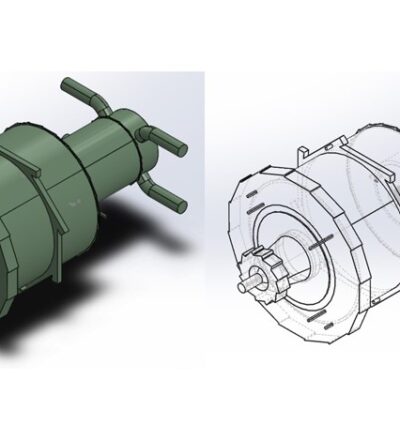
Spray drying is a crucial process in the food industry. It transforms various products into powders while preserving taste, aroma, and nutritional properties. Unfortunately, the process is also very energy intensive. In the Netherlands alone, it accounts for 15% of the industrial energy usage. However, a recent milestone achievement promises to revolutionize this energy-intensive practice.
The groundbreaking solution? The Radial Multizone Dryer (RMD) further developed by the Engender project. This is a compact and energy-efficient drying technology that combines high-G force and multizone operation. In this way, spray drying can be intensified. Compared to conventional methods, the Radial Multizone Dryer boasts a significantly reduced equipment footprint, leading to lower capital and operational expenses.
Energy savings up to 30%
The Engender project involved collaboration of Avebe, Corbion, Givaudan, UCLouvain and the University of Twente. Together they focused on optimizing the RMD’s operating parameters and design details. Through extensive testing and refinement, the team addressed challenges related to scalability, stability, and product quality. The experiments and simulations also proved substantial energy savings up to 20-30%.
Computational fluid dynamics
One of the key innovations introduced was the optimization of countercurrent flows using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. These modifications not only enhanced energy efficiency, but also improved product quality by controlling droplet and particle size distribution.
Future developments
Despite significant progress, challenges remain. In particular, scale-up and equipment simplification. The complexity of the current design requires collaboration with industrial equipment suppliers to develop a more streamlined solution. In addition, ensuring product quality and minimizing exposure to hot air remain key areas for future development.
Looking ahead, the ENGENDER project marks a critical step towards commercializing energy-efficient spray drying technology. With a focus on scaling up and refining the design based on project learnings, the journey towards a more sustainable and cost-effective future for the food industry continues.
Acknowledgement
This project is co-funded by TKI-Energy with the supplementary grant 'TKI- Toeslag' for Topconsortia for Knowledge and Innovation (TKI’s) of the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Policy.