The Institute for Sustainable Process Technology (ISPT), in cooperation with Hitachi Energy and consortium partners Equinor, HyCC, Ørsted, Port of Rotterdam, and Yara, has completed a feasibility study to explore a (hybrid) electrical layout, incorporating DC and AC connections. The study focuses on developing optimised power conversion schemes for a gigawatt (GW)-scale water electrolysis plant.
The objective is to prepare a conceptual design for a converter topology that enables the integration of this new electrical layout, highlighting both its benefits and limitations.
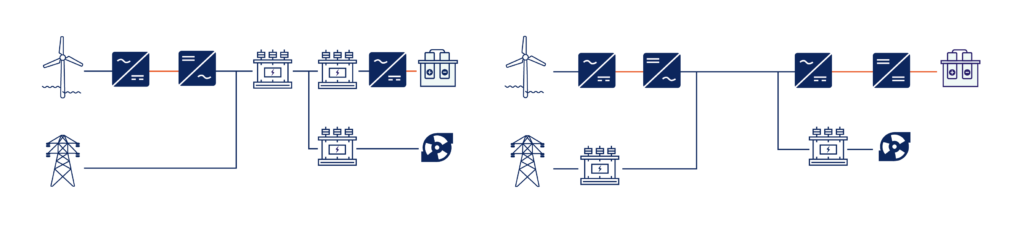
A new electrical layout with innovative power converters has been selected due to its relatively high maturity level, the suggested higher efficiency, the potential lowest complexity, costs, and footprint. It is recommended to further investigate the proposed innovative converters, optimizing the techno-economic size and feasibility, enhancing power quality, the galvanic isolation, and improving interfaces with the electrolysers.
Download the report to explore all the findings.
🎧 Prefer listening? Listen to this publication summarized in a 16-minute podcast, crafted using Google’s NotebookLM.
Download your free copy
Our publications are free to access. Simply provide your first name and email address to download.
